By: Nur Haziqah Binti Abdul Hamid and Nur Alifah Ilyana Binti Mohd Zakri (Industrial Trainee, Universiti Teknologi Mara Cawangan Negeri Sembilan, Kampus Rembau)
DEFINITION
- Research data management is a term that describes the organization, storage, preservation, and sharing of data collected and used in a research project. It involves the everyday management of research data during the lifetime of a research project for example, using consistent file naming conventions. It also involves decisions about how data will be preserved and shared after the project is completed for example, depositing the data in a repository for long-term archiving and access.
- RDM is a standard part of good research practice offering a lot of benefits to the society, research funders and the research community. Jones et al. (2013) gave the Digital Curation Centre definition of RDM as “the active management and appraisal of data over the lifecycle of scholarly and scientific interest”. It can help researchers by potentially increasing efficiency, saving time and resources and boosting the impact and visibility of their work through openness and transparency.
- A study by Smith (2014) observed that the challenge of how to effectively manage research data affects all scientists and researchers within and across multiple domains. The study observed further that most researchers struggle unsuccessfully with storage and management of their burgeoning volume of documents and data sets that they need and that result from their work. The consequence of this is that rising accumulation of useful findings may be lost or unavailable when conducting future research. There is, therefore, the need to incorporate a good data management practice throughout the research workflow.
TYPES
Research data can take many forms. It might be:
- Documents, spreadsheets
- Laboratory notebooks, field notebooks, diaries
- Questionnaires, transcripts, codebooks
- Audiotapes, videotapes
- Photographs, films
- Test responses
- Slides, artefacts, specimens, samples
- Collections of digital outputs
- Data files
- Database contents (video, audio, text, images)
- Models, algorithms, scripts
- Contents of an application input, output, log files for analysis
- software, simulation software, schemas
- Methodologies and workflows
- Standard operating procedures and protocol
RESEARCH DATA MANAGEMENT LIFECYCLE
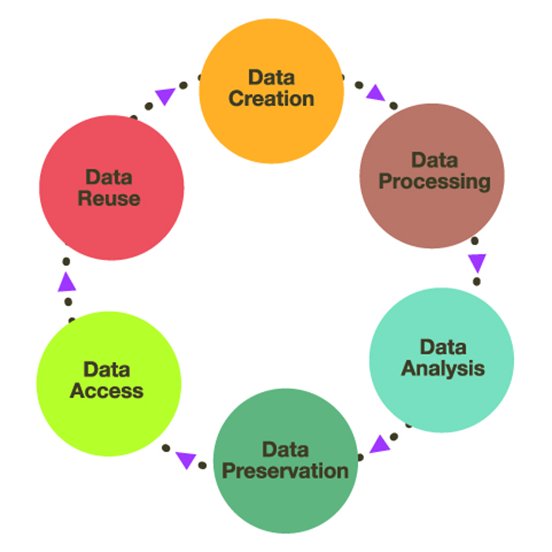
- This pictorial representation of Research Data Management indicates the best practice when it comes to managing research data. It begins at the top with Data Creation and moves clockwise through the process. After data is created, it is then processed and analyzed. Data should then be preserved into archival formats and made accessible to the public.This will enable reuse by other researchers who will then create their own data and the cycle will begin again. Though this cycle assumes that each stage will take place in its entirety before moving onto the next stage, practice dictates that there may be several iterations of creation, processing, and analysis before it is ready to be preserved.
WHY
Managing research data brings many benefits, not only to the project but to future researchers and wider society. The reason why research data management is used is because:
- Increases transparency
- Makes your data accessible
- Saves you time when writing up
- Reduces the risk of data loss
- Facilitates future reuse and sharing
- Improves citations.
References:
- https://library.leeds.ac.uk/info/14062/research_data_management/61/research_data_management_explained
- https://library.leeds.ac.uk/info/14062/research_data_management/61/research_data_management_explained
- Abduldayan, F.J., Abifarin, F.P., Oyedum, G.U. and Alhassan, J.A. (2021), "Research data management practices of chemistry researchers in federal universities of technology in Nigeria", Digital Library Perspectives, Vol. 37 No. 4, pp. 328-348. https://doi-org.ezaccess.library.uitm.edu.my/10.1108/DLP-06-2020-0051
- Palsdottir, A. (2021), "Data literacy and management of research data – a prerequisite for the sharing of research data", Aslib Journal of Information Management, Vol. 73 No. 2, pp. 322-341. https://doi-org.ezaccess.library.uitm.edu.my/10.1108/AJIM-04-2020-0110)
- https://pitt.libguides.com/managedata#:~:text=Research%20data%20management%20(or%20RDM,using%20consistent%20file%20naming%20conventions)
- Guides: Research Data Management (A How-to Guide): Research Data Management Definition. (2019). Retrieved May 23, 2022, from Depaul.edu website: https://libguides.depaul.edu/c.php?g=620925&p=4324498
Tarikh Input: 27/01/2023 | Kemaskini: 11/03/2024 | amiruliqhmal
PERKONGSIAN MEDIA













.png)





















